The role of ionomers in the electrolyte management of zero-gap MEA-based CO2 electrolysers: A Fumion vs. Nafion comparison
The paper authored by M. Liu H. Hu, Y. Kong, I. Zelocualtecatl Montiel, V. Kolivoška, A. Rudnev, Y. Hou, R. Erni,
S. Vesztergom and P. Broekmann
is published in Applied Catalysis B: Envrionmental (2023, vol. 335, pp. 122885).
Abstract:
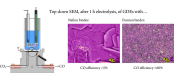
We study the role of binders (ionomers) in determining the life-span of gas diffusion electrodes (GDEs) used for high throughput CO2-to-CO electrolysis. We compare two typical ionomer materials (Nafion and Fumion, both are widely used for the preparation of Ag nanoparticles-based catalyst inks) to show that when used in zero-gap membrane/electrode assemblies, Fumion-containing inks are superior to Nafion-based ones and can uphold a very high CO-selectivity in the electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction for longer time. This is due to the ability of Fumion containing inks to suppress precipitation inside the GDE structure. As Fumion-fixed GDEs are significantly less hydrophobic than Nafion-fixed ones, our results contradict the widely accepted opinion that it is their non-wettability what mostly protects CO2-reducing GDEs from flooding. In turn, we argue that it is more important to maintain efficient electrolyte drainage pathways in the GDE structure, and explain the superiority of Fumion-fixed GDEs on this basis.
